
Diseased berries contain a white fungus growth that appears cottony.
OSU Extension Plant Pathology Slide Collection.
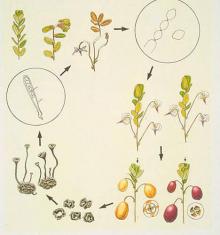
Disease cycle of Monilinia oxycocci on cranberry.
Courtesy of P. S. McManus, UW-Madison.

Growth of cottony fungal mycelium in the seed cavity of infected berries. Berries
on the right end of each row are healthy.
Courtesy of Peter Bristow, WSU-Puyallup.

The tip blight stage of the disease. Note the whitish-gray fungal growth on the stem."
Photo by Peter Bristow, WSU-Puyallup.

Apothecia arising from a sclerotium of M. oxycocci.
Photo by Peter Bristow, WSU-Puyallup.