Cause Several fungi including Godronia cassandrae (asexual: Fusicoccum putrefaciens), end rot; Phomopsis vaccinii, viscid rot; Botrytis sp., yellow rot; Allantophomopsis cytisporea and A. lycopodina, black rot; Glomerella cingulata (asexual Colletotrichum acutatum), bitter rot; Coleophoma empetri, ripe rot; Botryosphaeria vaccinii, berry speckle; and Physalospora vaccinii, blotch rot. Yeasts have also been shown to rot wet-harvested cranberries including Hanseniaspora uvarum, Pichia fermentans, and Pichia terricola. In the 2020s, Neofabraea actinidiae was found causing a fruit rot in Oregon cranberry beds.
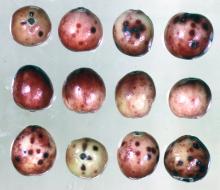
Fungi that cause fruit rots are in the beds and can be troublesome especially when rainy conditions persist during bloom. The two types of rot are field rots that develop before harvest, and postharvest rots that form after harvest in fresh fruit in refrigerated storage. Field rots have not been economically important in well-managed beds but levels are on the increase. Postharvest rots are important only for fresh fruit; frozen storage has eliminated them for processed fruit. Many of these fungi begin the infection process during bloom and symptoms may not be seen until fruit mature or after harvest. Floral extracts from susceptible cultivars increased appressorial formation and infection of fruit for those fungi that produce latent infections at bloom. Control of fruit rots in the field near fruit set reduces decay when fresh berries are held in refrigerated storage. Bacteria have not been shown to cause fruit rots. Cultivars that have fruit with more epicuticular wax have been associated with less fruit rot development.
Symptoms Any change in normal color or consistency of the berry during development such as softening, discoloring, or shriveling. Symptoms on fruit infected by different fungi are very similar, making it nearly impossible to distinguish between rots based on symptoms alone.
Symptoms associated with N. actinidiae on 'Stevens' cranberries often included softening and brown tissue surrounded by a yellow-colored ring.
Low temperature breakdown, from berries stored at freezing for over 2 weeks, is characterized by a dull external appearance and watersoaked or rubbery deep maroon flesh.
Cultural control
- Control weeds.
- Avoid over-fertilization, which favors rank vine growth.
- Avoid bruising fresh market fruit during harvesting, devining, and handling.
- The cultivars Pilgrim Stevens, Mullica Queen, and Scarlet Knight have some resistance to fruit rots and are high yielding.
Chemical control Three applications are recommended for field fruit rots. Control is based on protecting berries during bloom and from shortly after fruit set through the time when they are partially colored. Fungicides applied during bloom and shortly after fruit set are the most effective. Materials applied close to harvest are not very effective. Tank-mix and/or alternate products from different groups with different modes of action to prevent the build-up of resistant fungi.
For all markets:
- Abound at 6 to 15.5 fl oz/A. Do not apply within 3 days of harvest or with silicone-based surfactants. Do not apply to flooded crop or allow release of irrigation or flood waters for 14 days after application. Highly toxic to fish. Group 11 fungicide. 4-hr reentry.
- Aframe at 6 to 15.5 fl oz/A. May be applied day of harvest. Sprayers should not be used on apples. Group 11 fungicide. 4-hr reentry.
- Badge X2 at 3.5 to 7 lb/A. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry. O
- Champ WG at 4.2 lb/A. Extremely toxic to fish. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry.
- Cueva at 0.5 to 2 gal/100 gal water/A. Group M1 fungicide. 4-hr reentry. O
- Cuprofix Ultra 40 Disperss at 5 lb/A. Highly toxic to fish. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry.
- Dexter Max at 3.2 to 5 lb/A. Do not use within 30 days of harvest. Group M3 + 11 fungicide. 24-hr reentry.
- Evito 480 SC at 2 to 5.7 fl oz/A. Do not apply within 1 day of harvest. Group 11 fungicide. Highly toxic to fish. 12-hr reentry.
- Ferbam Granuflo at 6.1 lb/A. Do not apply within 28 days after mid-bloom. Toxic to fish. Group M3 fungicide. 24-hr reentry.
- Indar 2F at 6 to 12 fl oz/A plus a wetting agent. Do not use within 30 days of harvest. Moderately toxic to fish. Group 3 fungicide. 12-hr reentry.
- Kocide 50 DF at 4 lb/A. Highly toxic to fish. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry.
- Mancozeb products such as Dithane, Koverall, Manzate Pro-Stick, or Penncozeb 75 DF at 3 to 6 lb/A or 2.4 to 4.8 qt/A. Do not apply within 30 days of harvest. Can apply through several types of irrigation systems; see manufacturer's directions. Moderately toxic to fish. Group M3 fungicides. 24-hr reentry.
- ManKocide at 7 lb/A. Do not apply within 30 days of harvest. Can apply through several types of irrigation systems; see manufacturer's directions. Highly toxic to fish. Group M1 + M3 fungicide. 48-hr reentry.
- Mastercop at 3 pints/A. Toxic to fish. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry. O
- Nu-Cop 50 DF at 4.2 lb/A. Slightly toxic to fish. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry. O
- Oso SC at 6.5 to 13 fl oz/A. May be applied on the day of harvest. Group 19 fungicide. 4-hr reentry. O
- Ph-D WDG at 6.2 oz/A plus an adjuvant. Do not make more than three (3) applications/A/season. May be applied on the day of harvest. Group 19 fungicide. 4-hr reentry.
- Proline 480 SC at 5 fl oz/A. Use up to two (2) applications. Do not use within 45 days of harvest. Group 3 fungicide. 12-hr reentry.
- Quadris at 6 to 15.5 fl oz/A. Do not apply with silicone-based surfactants. May be applied on the day of harvest. Group 11 fungicide. 4-hr reentry.
- Quadris Top at 10 to 14 fl oz/A. Do not release irrigation water for 14 days after application or apply within 30 days of harvest. Sprayers should not be used on apples. Group 3 + 11 fungicide. 12-hr reentry.
- Quilt Xcel at 14 to 21 fl oz/A. If used earlier for cottonball then only use once at early bloom. Do not use on flooded fields, and do not release irrigation water for 14 days after application or apply within 45 days of harvest. Sprayers should not be used on apples. Group 3 + 11 fungicide. 12-hr reentry.
- Satori at 6 to 15.5 fl oz/A. May be applied day of harvest. Sprayers should not be used on apples. Group 11 fungicide. 4-hr reentry.
For domestic markets only: Growers can use chlorothalonil products if their fruit is destined for DOMESTIC markets. Growers should check with their handlers before using any formulation using this active ingredient.
- Chlorothalonil products are registered. Do not apply within 50 days of harvest. Applications in warm weather during or shortly after bloom may reduce yields (Wisconsin data). Do not apply within 25 ft of marine/estuarine water bodies or release irrigation water from beds for 3 days after application. Apply only through solid-set sprinkler irrigation systems. Highly toxic to fish. 12-hr reentry.
- Bravo Weather Stik at 4 to 6.5 pints/A.
- Bravo Ultrex at 3.8 to 6 lb/A.
- Echo 720 at 4 to 7 pints/A.
- Echo 90 DF at 3.25 to 5.75 lb/A.
- Equus 720 SST at 4 to 6.5 pt/A.
References Conti, M., Cinget, B., Vivancos, J., Oudemans, P.V., and Bélanger, R.R. 2019. A Molecular Assay allows the Simultaneous Detection of 12 Fungi Causing Fruit Rot in Cranberry. Plant Disease 103:2843-2850.
Valentine, D. C., Shaffer, B. T., McGhee, G. C., Bouska, C. and Stockwell, V. O. 2024. First Report of Neofabraea actinidiae Causing a Cranberry Fruit Rot in Oregon. Plant Disease, 108:1405-1406.
Waller, T. J., Gager, J., Constantelos, C., and Oudemans, P. V. 2020. The Role of Flowers in the Disease Cycle of Colletotrichum fioriniae and Other Cranberry Fruit Rot Fungi. Phytopathology, 110:1270-1279.
Zalewski, Z. D., Page, R., Lankau, R. A. and McManus, P. S. 2021. Role of yeasts in the cranberry fruit rot disease complex. Plant Disease, 105:2141-2148.