See:
Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) - Mummy Berry
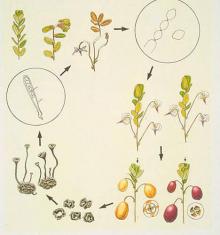
Cause Monilinia oxycocci, a fungus that overwinters in mummified berries from the previous season. Apothecia (spore cups) arise from these berries in the spring. Spores (ascospores) released from the cups infect new shoot growth in early spring, causing tip blight. Blighted shoot tips appear in June. Fruit infections are from a second, asexual spore type (conidia) produced on blighted shoot tips. This disease was a problem in Washington during the 1920s and 1930s but is rarely found now, except in British Columbia where it is still considered an economic problem.
Symptoms In the tip-blight stage of disease, young growing tips of new upright growth turn brown, curl over and wilt. Masses of whitish gray spores (conidia) form on a portion of the stem of the blighted upright. Affected berries remain yellowish-tan rather than coloring normally. In some cases, infected berries turn brown and shrivel before sizing up. Diseased berries also remain firm instead of becoming soft, as is the case with other fruit-rotting fungi. Diseased berry seed cavities contain a white, cottony fungus growth. Late in the season, fruits shrivel, harden and darken, and eventually mummify.
Cultural control
- Plant pathogen-free vines. If vines come from Wisconsin, make sure they do not come from a bed with a history of cottonball.
- 'McFarlin' and 'Stevens' are more resistant than either 'Bergman' or 'Pilgrim'.
- Flood or water harvesting removes many of the sclerotia. Reflooding beds, along with removal of floating plant debris, also reduces inoculum.
Chemical control Spray when buds break dormancy and again 1 to 2 weeks later and again during bloom. Under low disease pressure bloom sprays may be sufficient alone. Alternate or tank-mix fungicides from different groups that have different modes of action. Limit applications from any particular group to two (2) or fewer per year.
- Abound at 6 to 15.5fl oz/A. Do not apply within 3 days of harvest or with silicone-based surfactants. Do not apply to flooded crop or allow release of irrigation or flood waters for 14 days after application. Highly toxic to fish. Group 11 fungicide. 4-hr reentry.
- Badge X2 at 3.5 to 7 lb/A. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry. O
- Bordeaux mixture (8-8-100). Repeat at 2-week intervals. Moderately toxic to fish. Group M1 fungicide. O
- Champ WG at 4.2 lb/A. Extremely toxic to fish. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry.
- Cuprofix Ultra 40 Disperss at 5 lb/A. Highly toxic to fish. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry.
- Dexter Max at 3.2 to 5 lb/A. Do not use within 30 days of harvest. Group M3 + 11 fungicide. 24-hr reentry.
- Indar 2F at 6 to 12 fl oz/A plus a wetting agent. Do not use within 30 days of harvest. Moderately toxic to fish. Group 3 fungicide. 12-hr reentry.
- Nu-Cop 50 DF at 4.2 lb/A. Slightly toxic to fish. Group M1 fungicide. 48-hr reentry. O
- Oso SC at 6.5 to 13 fl oz/A. May be applied on the day of harvest. Group 19 fungicide. 4-hr reentry. O
- Proline 480 SC at 5 fl oz/A. Use up to two (2) applications. Do not use within 45 days of harvest. Group 3 fungicide. 12-hr reentry.
- Propiconazole-based fungicides are registered. Do not use within 45 days of harvest. Oregon and Washington only. Extremely toxic to fish. Group 3 fungicides.
- Bumper 41.8 EC at 4 to 6 fl oz/A. 12-hr reentry.
- Fitness at 4 to 6 fl oz/A. 12-hr reentry.
- PropiMax EC at 4 to 6 fl oz/A. 12-hr reentry.
- Tilt at 4 to 6 fl oz/A. 24-hr reentry.
- Quadris at 6 to 15.5 fl oz/A. Do not apply with silicone-based surfactants. May be applied on the day of harvest. Group 11 fungicide. 4-hr reentry.
- Quadris Top at 10 to 14 fl oz/A. Do not release irrigation water for 14 days after application or apply within 30 days of harvest. Sprayers should not be used on apples. Group 3 + 11 fungicide. 12-hr reentry.
- Quilt Xcel at 14 to 21 fl oz/A. Do not use on flooded fields, and do not release irrigation water for 14 days after application or apply within 45 days of harvest. Extremely toxic to fish. Group 3 + 11 fungicide. 12-hr reentry.
Reference McManus, P.S., Best, V.M., Voland, R.P., and Leininger, B.L. 1999. Sensitivity of Monilinia oxycocci to fenbuconazole and propiconazole in vitro and control of cranberry cottonball in the field. Plant Disease 83:445-450.