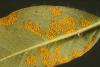
Cause Ascochyta rhei and Ramularia rhei, fungi that overwinter on old rhubarb leaves and stalks. These fungi also can spread through infected rootstock. Leaf spots are common on field-grown rhubarb west of the Cascade Range due to frequent rains in March and April when leaves and stalks are actively growing. Both pathogens produce spores that move by wind and splashing water.