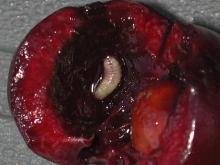
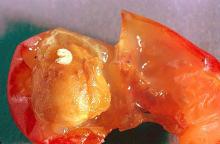
Rhagoletis indifferens
Pest description and crop damage Adults are somewhat smaller than a house fly and are about 0.2 inch in length. They have brownish to black wings with dark bands. White maggots infest cherries. The mature maggot makes a hole in the cherry as it exits. In the Northwest, the western cherry fruit fly infests both home-grown and commercial cherries. Western cherry fruit fly is also found in wild bitter cherry (Prunus emarginata).
Biology and life history The flies overwinter as pupae in the soil. The adult flies emerge from the soil from mid-May, about 5 weeks before harvest, until the end of July. Peak emergence often coincides with harvest. Adults feed on honeydew on leaves and pollen. After 7 to 10 days, females lay eggs under the skin of the fruit. The eggs hatch, and the larvae burrow toward the pit of the fruit. There they feed for 10 to 21 days before boring out and dropping to the ground to pupate. There is one generation per year. Adults emerge early the following season. A few pupae of western cherry fruit fly may remain in soil as long as 3 years.
Pest monitoring There is no tolerance for cherry fruit fly in cherry fruit, thus the threshold is zero. Degree-day models are used to determine first emergence in the major cherry production regions of the Pacific Northwest. Consult with your county Extension agent to determine the development of cherry fruit fly populations in your area. Yellow sticky traps hung in sunny parts of the tree will attract adults. Monitor daily.
Management-cultural control
Home orchardists: Grow early-maturing varieties such as 'Chelan.' Pick fruit within 8 to 9 days of catching the first flies, which will happen before egg hatch. Remove all fruit from the trees to eliminate sites for the fly to reproduce. Cultivation of the soil has not been effective, as the pupae are very hard-shelled.
Management-chemical control: HOME USE
Warning: Many pesticides are hazardous to bees. Look for bee precautionary statements on product labels and do not use these products during bloom or if bees are foraging in the orchard.
Begin spraying late May and continue through harvest. Spray at 10- to 21-day intervals. Degree-days can also be used to better determine fly emergence which is 950 degree-days after March 1.
- zeta-cypermethrin-Highly toxic to bees.
Management-chemical control: COMMERCIAL USE
Warning: These materials are hazardous to bees. Do not use during bloom or if bees are foraging in the orchard.
Growing-season sprays
- acetamiprid (Assail 70WP) at 2.3 to 3.4 oz/A. REI 12 hr. PHI 7 days.
- carbaryl (Carbaryl 4L) at 2 to 3 quarts/A (1 to 2 lb ai/A). REI 12 hr. PHI 3 days. Extremely toxic to aquatic invertebrates; avoid spray drift and runoff to surface waters. Apply at 7-day intervals no more than 3 times per year.
- diazinon (Diazinon 50W) at 1 lb/100 gal water. Do not exceed 4 lb/A per year (2 lb ai/A per year). REI 4 days. PHI 21 days. Do not exceed one in-season application per year.
- esfenvalerate (Asana XL) at 4.8 to 14.5 fl oz/A. REI 12 hr. PHI 14 days. May aggravate spider mite problems. Extremely toxic to fish and aquatic invertebrates; avoid spray drift and runoff to surface waters.
- imidacloprid (Prey 1.6F) at 8 fl oz/A. REI 12 hr. PHI 7 days. Do not use until pollination is complete and bees are no longer present.
- malathion (Malathion 57EC) at 1 pint/A. REI 12 hr. PHI 3 days. May injure certain varieties of sweet cherries. Malathion sprays may be less hazardous to bees.
- malathion (Fyfanon ULV Ag) at 16 oz/A. REI 12 hr. PHI 1 day. Maximum applications per season: sweet cherries- 4; tart cherries- 6. Repeat treatments after heavy rain if label allows.
- spinetoram (Delegate WG) at 6 to 7 oz/A. REI 4 hr. PHI 7 days. Maximum four applications per season. Do not apply more than a total of 28 oz of Delegate WG (0.438 lb ai spinetoram) per acre per year.
- spinosad (Entrust SC) at 4 to 8 fl oz/A (0.06 to 0.12 lb ai/A). REI 4 hr. PHI 7 days. Do not exceed 0.45 lb ai/A spinosad per year. OMRI-listed for organic use.
- Spinosad (GF-120) at 20 oz/A. REI 4 hr. Apply in spring with emergence of adult flies. Do not use for control of spotted wing drosophila.
- thiamethoxam (Actara) at 4.5 to 5.5 oz. REI 12 hr. PHI 14 days. Repeated applications may cause spider mite buildup. Do not exceed a total of 11.0 oz/Acre (0.172 lb ai/A) of Actara or 0.172 lb ai of thiamethoxam-containing products per acre per growing season.
Postharvest spray
- dimethoate (Dimethoate 400EC) at 1 quart/A. REI 10 days (REI 14 days in areas with less than 25 inches/year). One post-harvest application permitted in Oregon, Idaho, and Washington. Do not feed or graze livestock on cover crops in treated orchards. Do not mix with Syllit.