By L. Sims
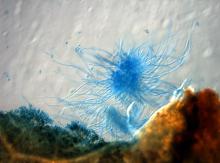
Cause Mycopappus alni (formerly Cercosporella alni) an ascomycete leaf pathogen forming filamentous conidia bunched in a mop-like mass. The conidial mass is held together by fungal stromatic tissue embedded in the leaf. These spore tufts are splash dispersed and readily dislodge from stromatic tissue by rain, dew or fog. Observed on red alders in Washington, Oregon, and on Vancouver Island, BC.
Symptoms Leaves form large brown blotches or spots without a well-defined edge. A whitish crust of fungal tissue can often be seen in the center of the leaf spot. Often causes early abscission of leaves and defoliation of trees.
Cultural control None are specifically listed but the following may be helpful in a nursery or landscape.
- Rake and destroy fallen leaves.
- Maintain tree vigor with adequate water and fertilizer.
- Space trees out in nursery production for good air circulation.
- Avoid overhead irrigation that keeps plants wet for an extended period of time.
Chemical control Applied before rains to protect new growth if needed.
- Eagle 20 EW at 6 to 12 fl oz/100 gal water. Group 3 fungicide. 24-hr reentry.
- Myclobutanil 20 EW T&O at 6 to 12 fl oz/100 gal water plus spreading agent. May observe a PGR effect. Group 3 fungicide. 24-hr reentry.
- Spectracide Immunox Multi-Purpose Fungicide Spray Concentrate for Gardens at 1 fl oz/gal water. Group 3 fungicide. H
References Redhead S.A., and White, G.P. 1985. Mycopappus, a new genus of leaf pathogens, and two parasitic Anguillospora species. Can. J. Bot. 63: 1429-1435.
Funk, A. 1985. Foliar Fungi of Western Trees. Canadian Forestry Service. Pacific Forest Research Center. pp 27.