Synanthedon bibionipennis
Pest description and crop damage The adult strawberry crown moth is a clear-winged moth about 12 mm in length that, like the raspberry crown borer, is black and yellow and resembles a yellowjacket wasp. Unlike raspberry crown borer larvae, strawberry crown moth larvae don't bore into canes but are found and feed on the outside of crowns and upper roots. Young larvae are all white. As they mature, they are white with a brown head; during the growing season, when they are actively feeding, they can take on a pinkish color. Mature larvae are up to 25 mm in length. Larval feeding weakens the caneberry plant and can reduce vigor, especially in young plantings. Individual canes within a hill may be affected.
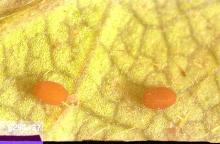
Biology and life history This insect completes its life cycle in one year. The larva overwinters in a silken cocoon covered with frass on the crown or upper roots of the plant. The larva leaves the cocoon and resumes feeding in spring. Pupation occurs from May to July; adults emerge and can be seen flying in June and July. Mating occurs shortly after emergence and females begin laying eggs singly on the leaf margins of lower leaves. Eggs are brown, oval-shaped, and have a lateral concave depression. Newly hatched larvae emerge in about two weeks, drop or crawl to the crown of the plant, and feed until the fall; they are nearly mature as they form a silken cocoon in which to overwinter.
Scouting and thresholds Pheromone traps are used to monitor adult male emergence and flight. This moth flies low so traps should be placed in several places throughout the planting at about 1.5 to 2 feet above the ground beginning in early May. When two or three adults are caught in traps in two or more consecutive days, treatment application may be necessary and are made about two weeks after a consistent trap count is achieved.
Management-chemical control: HOME USE
- bifenthrin
Management-chemical control: COMMERCIAL USE
- diazinon (several brands) at 2 lb ai/A. Apply as a crown drench in late March or before budbreak. Use 100 to 300 gal/A drench, directing spray toward crown and lower portion of canes. Rain should follow to move insecticide into the root zone where the larvae feed. One application per season allowed. Restricted use pesticide.
Note: Soil-applied bifenthrin (Brigade) and chlorantraniliprole (Altacor) in the spring for control of raspberry crown borer larvae may help control strawberry crown moth larvae.