Cause Bacterial brown spot is caused by the bacterium, Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae, which can overwinter on bean and several leguminous weed species. It can also contaminate seed, but the role of such inoculum in disease development is not well understood. Sprinkler irrigation and leaf rubbing can spread the disease. Data from the University of Wisconsin indicate that disease development correlates with the intensity of water droplet impacts on leaves. The disease usually is more of a problem in lima beans than in snap green beans. This disease was a problem in Idaho in 1995-97, primarily in sprinkler-irrigated fields, but has not been detected there the past several years. It is not a serious problem in Oregon's Willamette Valley but is a problem in Midwestern bean-producing areas where it overwinters on vetch. Strains of P. syringae that cause diseases of fruit crops will not cause brown spot on beans.
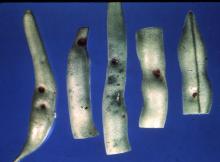
Symptoms Small round to oval, brownish red spots, often with a yellow halo, develop on leaves. Lesions may fall out, giving a shothole appearance. Under most conditions there is a little water soaking in the leaf. When the pathogen infects systemically, stems may have lesions. Lesions on pods are small, brownish red, oval spots preceded by small water-soaked spots. Pods may be twisted or bent from lesions.
Cultural control
- Control weeds, volunteer beans, and other plants that may serve as reservoirs for the pathogen.
- Plant pathogen-free seed if available.
- Use resistant varieties if available.
Chemical control
- Copper formulations (Group M1) offer limited control.
- Badge SC at 0.5 to 2 pints/A on 7- to 14-day intervals. Preharvest interval is 0 days. 48-hr reentry.
- Bonide Liquid Copper is available for home gardens. H
- Champ WG at 1.58 lb/A on 7- to 14-day intervals. 48-hr reentry. O
- Cueva at 0.5 to 2 gal/100 gal water on 7- to 10-day intervals. May be applied on the day of harvest. 4-hr reentry. O
- Previsto at 1 to 2 quarts/A on 7- to 14-day intervals. 48-hr reentry. O