Includes
Armyworns
Armyworm (Pseudaletia unipuncta)
Beet armyworm (Spodoptera exigua)
Loopers
Alfalfa looper (Autographa californica)
Cabbage looper (Trichoplusia ni)
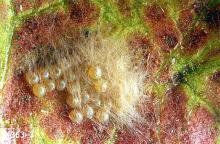
Pest description and crop damage Armyworm eggs are distinctive in their cottony masses. Young armyworms are small and green like loopers, but feed en masse and will leave several small holes. Loopers are green, smooth-skinned, and usually have a narrow stripe along each side. Looper caterpillars can be distinguished from other common caterpillars by their distinctive looping movement, in which they arch the middle portion of their body to bring the hind legs forward to meet the front legs. Larvae feed on leaves, causing ragged-edged holes in the leaf and on the leaf margins. Cabbage looper can cause severe damage from the inside out, producing a brown head that never opens, causing severe defoliation. Adults moths of loopers have brownish wings with distinctive dogleg figures on the front wings.
Management-chemical control
Begin applications at first sign of infestation. Multiple applications with thorough coverage are necessary for effective control.
Armyworms
- azadirachtin (Neemix 4.5) at 4 to 16 fl oz/A (0.012 to 0.047 lb ai/A). PHI 0 days. REI 4 hr. This botanical pesticide acts slowly. Spray early-well before harvest-and check for effect. Apply every 7 to 10 days or as needed. Some formulations are OMRI-listed for organic production.
Loopers
- azadirachtin (Neemix 4.5) at 7 to 16 fl oz/A (0.021 to 0.049 lb ai/A). REI 4 hr. PHI 0 days. This botanical pesticide acts slowly. Spray early-well before harvest-and check for effect. Apply every 7 to 10 days or as needed. Some formulations are OMRI-listed for organic production.