Aspila (Grapholita) molesta
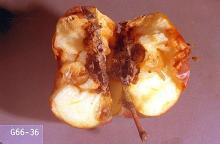
Pest description and crop damage Adult is a greyish brown moth with a wingspan of around 0.5 inch. Larvae are pinkish and between 0.4 to 0.5 inch in length when fully grown. Larvae tunnel within twigs and cause tips to wilt. This damage can be confused with peach twig borer but can be distinguished by observing the features of mature larvae. There are multiple generations each growing season. In later generations, larvae can attack the fruit, often by boring through the stem end into the fruit.
Biology and life history This insect overwinters as fully grown larvae in a hibernaculum (enclosed within a silk webbing) in ground cover or tree crevices. In spring, pupation occurs, and adults appear near bloom. Eggs are laid on foliage and the larvae feed by boring into the growing shoots. There may be 3 to 4 generations per year. Later generations also attack fruit before seeking overwintering sites.
Pest monitoring Distribution of this pest appears to be spotty in the Pacific Northwest with isolated populations found primarily in neglected backyard fruit trees. In fruit trees with a confirmed history of Oriental fruit moth infestations, scout fruit trees in early spring for wilted leaves at shoot and twig tips. Monitoring traps baited with Oriental fruit moth pheromone can be used to detect the absence/presence of this pest in your area and help better time pesticide applications.
Management-biological control
Dispensers containing synthetic insect pheromone may be used to disrupt Oriental fruit moth mating. Pheromone mating disruption works best in large orchard blocks and is not considered an option for backyard fruit trees. Expert advice and careful monitoring are necessary to use this product successfully.
Management-chemical control
Spray applications and pesticide residues must be well-timed to contact the newly hatched larvae before they bore into the shoot or fruit.
Management-chemical control: HOME USE
- acetamiprid
- azadirachtin (neem extract)-Some formulations are OMRI-listed for organic use.
- carbaryl-Highly toxic to bees.
- esfenvalerate-Highly toxic to bees.
- gamma-cyhalothrin-Highly toxic to bees.
- kaolin clay-Repels some insect pests when applied as a spray to leaves, stems, and fruit. OMRI-listed for organic use.
- lambda-cyhalothrin-Highly toxic to bees.
- pyrethrins-Some formulations are OMRI-listed for organic use.
- spinosad-Highly toxic to bees. Some formulations are OMRI-listed for organic use.
- zeta-cypermethrin-Highly toxic to bees.
Management-chemical control: COMMERCIAL USE
Spring applications
Dispensers must be in the orchard before adults begin flying in spring. Place dispensers in the upper one-third of the tree or higher. Some formulations are OMRI-listed for organic use.
- CheckMate OFM Dispenser at 100 to 200 dispensers/A. Some dispensers are OMRI-listed for organic use.
- Isomate OFM/PTB TT at 100 to 200 dispensers/A. Some dispensers are OMRI-listed for organic use.
Spring and summer sprays
Multiple sprays are necessary to control this pest because it has three to four generations per year. Apply sprays based on pheromone trap catches or apply at petal fall, again 10 to 12 days later, and a third time about mid-June.
- acetamiprid (Assail 70WP) at 2.3 to 3.4 oz/A. REI 12 hr. PHI 7 days.
- carbaryl (Carbaryl 4L) at 2 to 3 quarts/A. REI 12 hr. PHI 3 days. Extremely toxic to aquatic invertebrates; avoid spray drift and runoff to surface waters.
- chlorantraniliprole (Altacor 35 WDG) at 3 to 4.5 oz/A. REI 4 hr. PHI 10 days.
- flubendiamide/buprofezin (Tourismo) at 14 fl oz /A. REI 12 hr. PHI 14 days.
- methoxyfenozide (Intrepid 2F) at 10 to 16 fl oz/A. REI 4 hr. PHI 7 days.
- phosmet (Imidan 70-W) at 2.13 to 4.25 lb/A. Do not exceed 4.25 lb/A. REI 7 days. PHI 14 days. Not to exceed 4.25 lb product or 3 lb ai/A per year. REI 7 days. PHI 14 days. Extremely toxic to fish; avoid spray drift and runoff to surface waters.
- spinetoram (Delegate WG) at 6 to 7 oz/A. REI 4 hr. PHI 1 day.
- spinosad (Entrust 80W) at 1.25 to 2.5 oz/A. REI 4 hr. PHI 1 day. Results are best when applied at petal fall. OMRI-listed for organic use. May act slowly.