Pennisetia marginatum
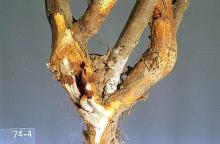
Pest description and crop damage The larvae of this insect bores into and damages the lower canes and crowns of most commercial caneberry species, as well as wild Rubus species like thimbleberry and salmonberry. The adult is a clear-winged moth with a yellow and black striped body that looks like a yellow jacket. The larvae are white with a brown head; when mature, they can be up to 38 mm in length. Boring into the canes by larvae reduces cane vigor, and canes may break off at ground level. Individual canes within a hill may be affected. Feeding within the canes weakens blackcaps, boysenberries, loganberries, and blackberries, and may kill raspberries, if populations are large.
Biology and life history The life cycle of this insect requires two years to complete. Adults can be seen flying from late July through October. Eggs are laid on the underside or edges of leaves, are brownish orange in color as they mature, and hatch in 30 to 60 days. Larvae crawl to the base of the cane and form overwintering cells. In spring, the larvae feed for a few weeks then bore into the cane, where their feeding causes galls or swelling at or below the soil surface. Larvae overwinter the second year in the canes. The fully-grown larvae continue to feed within the cane until June or July, and then pupate. The adults emerge from exit holes in the canes beginning in July. Generations overlap, and small and large larvae can be found in canes in April and May.
Scouting and thresholds Galls caused by larval feeding are particularly noticeable in October near the base of the plant. Look for brittle, hollow canes when tying up canes in the spring. During the growing season, individual canes may wilt or flag, indicating an infestation. There is very little tolerance for this pest, as a minor infestation can quickly become major.
Management-cultural control
Dig out and burn infested canes and crowns in the fall. Remove other hosts, such as wild blackberries, from the area.
Management-chemical control: HOME USE
No products are registered for home use for this pest
Management-chemical control: COMMERCIAL USE
Apply one of the following products as a crown drench in late March or before bud break. Use 100 to 300 gal/A, directing spray toward crown and lower portion of canes. Rain should follow to move insecticide into the root zone where the young larvae are feeding.
- bifenthrin (Brigade 2EC and others) at 0.1 lb ai/A. PHI 3 days. Only one pre-bloom application of bifenthrin is allowed in caneberries: either soil-applied for crown borer control or foliar-applied for root weevil or leafroller control, but not both. Restricted use pesticide.
- chlorantraniliprole (Altacor) at 0.066 to 0.099 lb ai/A. PHI 3 days. Do not exceed 0.2 lb ai/A per crop season.
- diazinon (several brands) at 2 lb ai/A. One application per season allowed. Restricted use pesticide.